-
Can smart cameras improve evacuations? A new approach to smarter crowd mapping
 Emergency evacuations during natural disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis increasingly rely on advanced technology to effectively assess real-time crowd movement and points of congestion. Disaster-preparedness involves the development of an optimized technology that is easy to use and interpret.... Read more
Emergency evacuations during natural disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis increasingly rely on advanced technology to effectively assess real-time crowd movement and points of congestion. Disaster-preparedness involves the development of an optimized technology that is easy to use and interpret.... Read more -
'Solar battery' stores sunlight for days, then releases hydrogen on demand
 A new material can store energy from sunlight and convert it into hydrogen days later. The material, jointly developed by researchers from Ulm and Jena, can do this even in the dark. The process is reversible and can be reactivated several times using a pH switch. The results are published... Read more
A new material can store energy from sunlight and convert it into hydrogen days later. The material, jointly developed by researchers from Ulm and Jena, can do this even in the dark. The process is reversible and can be reactivated several times using a pH switch. The results are published... Read more -
Swarming microrobots use spinning flows to turn gears without touching
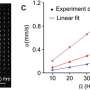 E pluribus unum—"out of many, one"—is not only a motto for the United States; it's a good credo for microrobots. A research collaboration between Cornell and the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems has shown how a swarm of microrobots spinning on a water surface can together generate the fluidic... Read more
E pluribus unum—"out of many, one"—is not only a motto for the United States; it's a good credo for microrobots. A research collaboration between Cornell and the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems has shown how a swarm of microrobots spinning on a water surface can together generate the fluidic... Read more -
The latest advances in pyrochlore oxide-based dielectric energy storage technology
 Pyrochlore oxides—a class of advanced dielectric materials—represent a promising next-generation approach to efficient energy storage. Their structural flexibility and tunable chemical composition make them prime candidates for dielectric energy storage applications.... Read more
Pyrochlore oxides—a class of advanced dielectric materials—represent a promising next-generation approach to efficient energy storage. Their structural flexibility and tunable chemical composition make them prime candidates for dielectric energy storage applications.... Read more -
Water-based enzyme ink enables one-step printing of wearable biofuel cells
 Enzymatic biofuel cells can act as self-powered wearable biosensors by converting chemicals in body fluids into electricity; however, manufacturing challenges have prevented their widespread adoption. Now, researchers from Japan have developed water-based 'enzyme inks' that enable single-step screen printing of complete biofuel cells onto paper substrates. The printed electrodes demonstrated... Read more
Enzymatic biofuel cells can act as self-powered wearable biosensors by converting chemicals in body fluids into electricity; however, manufacturing challenges have prevented their widespread adoption. Now, researchers from Japan have developed water-based 'enzyme inks' that enable single-step screen printing of complete biofuel cells onto paper substrates. The printed electrodes demonstrated... Read more -
Solvent‑free perovskite solar cell technology could pave way for scalable production
 Researchers at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed a multi-source co-evaporation recipe that markedly enhances the crystal quality of vacuum-deposited perovskite films. This advance brings all vacuum-deposited single-junction perovskite cells as well as perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells closer to scalable production. The research has been... Read more
Researchers at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed a multi-source co-evaporation recipe that markedly enhances the crystal quality of vacuum-deposited perovskite films. This advance brings all vacuum-deposited single-junction perovskite cells as well as perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells closer to scalable production. The research has been... Read more -
Hybrid perovskite device generates electricity from the sun and rain simultaneously
 A team from the Institute of Materials Science of Seville (ICMS), a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the University of Seville (US), has developed a new hybrid device that allows energy to be captured from both the sun and rain simultaneously. A thin film created... Read more
A team from the Institute of Materials Science of Seville (ICMS), a joint center of the Spanish National Research Council (CSIC) and the University of Seville (US), has developed a new hybrid device that allows energy to be captured from both the sun and rain simultaneously. A thin film created... Read more -
Borrowing from biology to power next-gen data storage
 DNA, the genetic blueprints in every living organism, is nature's most efficient storage mechanism, capable of storing about 215 million gigabytes of data per gram. That storage capacity, if applied to electronics, could enable significantly more efficient data centers, speedier data processing and the ability to process far more complicated... Read more
DNA, the genetic blueprints in every living organism, is nature's most efficient storage mechanism, capable of storing about 215 million gigabytes of data per gram. That storage capacity, if applied to electronics, could enable significantly more efficient data centers, speedier data processing and the ability to process far more complicated... Read more -
A new eco-friendly water battery could theoretically last for centuries
 The problem with many types of modern batteries is that they rely on harsh chemicals to work. Not only can these corrosive liquids damage internal parts over time, but they can also leach into soil and water when disposed of, contaminating it. But researchers from the City University of Hong... Read more
The problem with many types of modern batteries is that they rely on harsh chemicals to work. Not only can these corrosive liquids damage internal parts over time, but they can also leach into soil and water when disposed of, contaminating it. But researchers from the City University of Hong... Read more -
A heatshield for 'never-wet' surfaces: Engineers repel even near-boiling water with low-cost, scalable coating
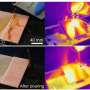 Superhydrophobic surfaces—those famously "never-wet" materials that make water bead up and roll away—have a stubborn weakness: hot water. Once temperatures climb above roughly 40 degrees Celsius, many superhydrophobic coatings abruptly lose their magic. Instead of skittering off, hot droplets start sticking, soaking into the surface texture and leaving behind wet... Read more
Superhydrophobic surfaces—those famously "never-wet" materials that make water bead up and roll away—have a stubborn weakness: hot water. Once temperatures climb above roughly 40 degrees Celsius, many superhydrophobic coatings abruptly lose their magic. Instead of skittering off, hot droplets start sticking, soaking into the surface texture and leaving behind wet... Read more -
Engineers discover new physics principle to break sound absorption barriers in ventilated spaces
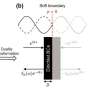 In everyday life, designing spaces that both let air flow and absorb sound can be a tricky balancing act. Usually, materials that allow air to pass through—like vents—also let sound escape, making it hard to reduce noise effectively. Conversely, sound-absorbing materials like foam often block airflow, limiting their use in... Read more
In everyday life, designing spaces that both let air flow and absorb sound can be a tricky balancing act. Usually, materials that allow air to pass through—like vents—also let sound escape, making it hard to reduce noise effectively. Conversely, sound-absorbing materials like foam often block airflow, limiting their use in... Read more -
Quantum materials could enable the solar-powered production of hydrogen from water
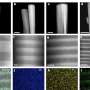 Hydrogen fuel is a promising alternative to fossil fuels that only emits water vapor when used and could thus help to lower greenhouse gas emissions on Earth. In the future, it could potentially be used to fuel heavy-duty transport vehicles, such as trucks, trains, and ships, as well as industrial... Read more
Hydrogen fuel is a promising alternative to fossil fuels that only emits water vapor when used and could thus help to lower greenhouse gas emissions on Earth. In the future, it could potentially be used to fuel heavy-duty transport vehicles, such as trucks, trains, and ships, as well as industrial... Read more -
Shipping damage, measured in real time: How wireless origami cushioning could improve logistics
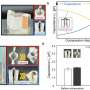 Origami, the traditional Japanese art of paper folding, has received considerable attention in engineering. By applying paper-folding principles, researchers have created compact structures that are flexible, lightweight, and reconfigurable across aerospace, medicine, and robotics.... Read more
Origami, the traditional Japanese art of paper folding, has received considerable attention in engineering. By applying paper-folding principles, researchers have created compact structures that are flexible, lightweight, and reconfigurable across aerospace, medicine, and robotics.... Read more -
Hot cities, safer buildings: A cooling coating that can also reduce fire risk
 An international research team has demonstrated how conventional radiative cooling coatings can be optimized to further reduce building surface temperatures, cutting energy consumption, while also improving fire safety.... Read more
An international research team has demonstrated how conventional radiative cooling coatings can be optimized to further reduce building surface temperatures, cutting energy consumption, while also improving fire safety.... Read more -
This special solar cell system produces both electricity and heat
 Researchers have developed a solar cell system that uses mirrors to concentrate solar energy. In addition to electricity, it produces heat for a plant that will capture carbon from industrial emissions. The solar cells in the large pilot plant are a full 5 meters high and consist of many mirrors... Read more
Researchers have developed a solar cell system that uses mirrors to concentrate solar energy. In addition to electricity, it produces heat for a plant that will capture carbon from industrial emissions. The solar cells in the large pilot plant are a full 5 meters high and consist of many mirrors... Read more -
Laser-etched glass can store data for 10,000 years, Microsoft says
 Thousands of years from now, what will remain of our digital era? The ever-growing vastness of human knowledge is no longer stored in libraries, but on hard drives that struggle to last decades, let alone millennia.... Read more
Thousands of years from now, what will remain of our digital era? The ever-growing vastness of human knowledge is no longer stored in libraries, but on hard drives that struggle to last decades, let alone millennia.... Read more -
New tech and AI set to take athlete data business to next level
 From tracking the trajectory and speed of a footballer's strike to monitoring a Tour de France rider's real-time power output, performance athlete data is deepening its reach in sports, with specialized firms eyeing to score big business.... Read more
From tracking the trajectory and speed of a footballer's strike to monitoring a Tour de France rider's real-time power output, performance athlete data is deepening its reach in sports, with specialized firms eyeing to score big business.... Read more -
From automated farm tractors to exam paper grading, AI boosts efficiency for some in India
 Farmer Bir Virk tapped the iPad mounted beside his tractor's steering wheel and switched the vehicle to automatic mode. The machine moved forward and began harvesting potatoes on its own in the fields of Karnal, a city in northern India.... Read more
Farmer Bir Virk tapped the iPad mounted beside his tractor's steering wheel and switched the vehicle to automatic mode. The machine moved forward and began harvesting potatoes on its own in the fields of Karnal, a city in northern India.... Read more -
Repairable infrared lens can cut costs and bring thermal imaging to more devices
 The days of dropping a thermal imaging camera and replacing an expensive lens are coming to an end with a new repairable lens developed by Flinders University scientists. The high-performance lens for infrared cameras invented by Flinders researchers is emerging as a lower cost, more sustainable option for industries which... Read more
The days of dropping a thermal imaging camera and replacing an expensive lens are coming to an end with a new repairable lens developed by Flinders University scientists. The high-performance lens for infrared cameras invented by Flinders researchers is emerging as a lower cost, more sustainable option for industries which... Read more -
Operando X-rays reveal key aging process in sodium-zinc molten salt batteries
 Up to now, it has only been possible to deduce indirectly why high-temperature batteries lose efficiency and durability while in use. For the first time, a team from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) has now used operando X-ray radiography to look directly into a sodium-zinc molten salt battery at approximately 600... Read more
Up to now, it has only been possible to deduce indirectly why high-temperature batteries lose efficiency and durability while in use. For the first time, a team from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Dresden-Rossendorf (HZDR) has now used operando X-ray radiography to look directly into a sodium-zinc molten salt battery at approximately 600... Read more -
NASA advances high-altitude traffic management
 High-altitude flight is getting increasing attention from sectors ranging from telecommunications to emergency response. To make that airspace more accessible, NASA is developing an air traffic management system covering those altitudes and supplementing its work with real-time data from a research balloon in Earth's stratosphere.... Read more
High-altitude flight is getting increasing attention from sectors ranging from telecommunications to emergency response. To make that airspace more accessible, NASA is developing an air traffic management system covering those altitudes and supplementing its work with real-time data from a research balloon in Earth's stratosphere.... Read more -
Converting human urine into clean energy: Researchers optimize the process
 Researchers at McGill University have improved the efficiency of a method for converting human urine into clean energy. The method employs microbial fuel cells (MFCs), which use bacteria to turn organic waste into electricity, providing a sustainable and low-cost means of treating wastewater while generating energy from an abundant source.... Read more
Researchers at McGill University have improved the efficiency of a method for converting human urine into clean energy. The method employs microbial fuel cells (MFCs), which use bacteria to turn organic waste into electricity, providing a sustainable and low-cost means of treating wastewater while generating energy from an abundant source.... Read more -
Ultrafast 3D printing method creates complex objects in under a second
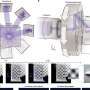 High-speed 3D printing has just gotten a lot faster. Researchers from Tsinghua University in China have developed a new high-speed printing technology capable of creating complex millimeter-scale objects in just 0.6 seconds. Traditional 3D printing is often slow because it builds objects one thin layer at a time. While a... Read more
High-speed 3D printing has just gotten a lot faster. Researchers from Tsinghua University in China have developed a new high-speed printing technology capable of creating complex millimeter-scale objects in just 0.6 seconds. Traditional 3D printing is often slow because it builds objects one thin layer at a time. While a... Read more -
The giant fire tornado that could save our oceans
 In the frantic hours following an offshore oil spill, emergency responders face a destructive decision: let the oil spread or ignite it. Once ignited, it creates an "in-situ" fire pool that stops the oil from spreading and poisoning marine ecosystems—but it comes at a heavy cost. Thick, black smoke billows... Read more
In the frantic hours following an offshore oil spill, emergency responders face a destructive decision: let the oil spread or ignite it. Once ignited, it creates an "in-situ" fire pool that stops the oil from spreading and poisoning marine ecosystems—but it comes at a heavy cost. Thick, black smoke billows... Read more -
Fiber batteries promise 'smart clothing,' but two obstacles stand in the way
 Fiber batteries are an emerging technology which could one day be used to create smart clothing with a wide array of functions, from charging electronic devices to acting as wearable controllers. However, a new study finds scientists have two major obstacles to overcome before the technology is ready for practical... Read more
Fiber batteries are an emerging technology which could one day be used to create smart clothing with a wide array of functions, from charging electronic devices to acting as wearable controllers. However, a new study finds scientists have two major obstacles to overcome before the technology is ready for practical... Read more -
Woven nickel-titanium structures unlock new flexibility in 3D-printed shape-memory materials
 At first glance, few materials would seem to have less in common than metals and textiles. And yet, by manufacturing nickel-titanium alloys as a highly deformable, interwoven material, more similar to fabric than a typical metal component, researchers from IMDEA Materials Institute and the Technical University of Madrid (UPM) have... Read more
At first glance, few materials would seem to have less in common than metals and textiles. And yet, by manufacturing nickel-titanium alloys as a highly deformable, interwoven material, more similar to fabric than a typical metal component, researchers from IMDEA Materials Institute and the Technical University of Madrid (UPM) have... Read more -
Midair haptics and levitation may get steadier with predictable ultrasonic airflow
 Acoustic streaming generated by airborne ultrasonic phased arrays plays a critical role in the performance of advanced ultrasonic technologies, including midair haptic feedback, odor delivery, and acoustic levitation. Researchers at University of Tsukuba have developed a predictive model for acoustic streaming in phased arrays by integrating three-dimensional acoustic and fluid... Read more
Acoustic streaming generated by airborne ultrasonic phased arrays plays a critical role in the performance of advanced ultrasonic technologies, including midair haptic feedback, odor delivery, and acoustic levitation. Researchers at University of Tsukuba have developed a predictive model for acoustic streaming in phased arrays by integrating three-dimensional acoustic and fluid... Read more -
Rule-breaking discovery reveals new way to strengthen metal in extreme conditions
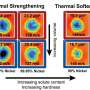 There's a reason why blacksmiths fire metals before hammering them. Heat always softens metal, making it more malleable and easier to reshape. Or does it? In a surprising new study, Northwestern University engineers discovered that, in extreme conditions, heat doesn't soften pure metals—it strengthens them.... Read more
There's a reason why blacksmiths fire metals before hammering them. Heat always softens metal, making it more malleable and easier to reshape. Or does it? In a surprising new study, Northwestern University engineers discovered that, in extreme conditions, heat doesn't soften pure metals—it strengthens them.... Read more -
Lithium alternatives? Calcium-ion batteries show strong 1,000-cycle performance in new test
 Researchers at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have achieved a breakthrough in calcium-ion battery (CIB) technology, which could transform energy storage solutions in everyday life. Utilizing quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs), these innovative CIBs promise to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of energy storage, impacting a wide range... Read more
Researchers at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have achieved a breakthrough in calcium-ion battery (CIB) technology, which could transform energy storage solutions in everyday life. Utilizing quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs), these innovative CIBs promise to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of energy storage, impacting a wide range... Read more -
How much can an autonomous robotic arm feel like part of the body?
 When AI-powered prosthetic arms that move autonomously become widespread, understanding how people feel about them and accept them will be crucial. In a study appearing in Scientific Reports, scientists used virtual reality to simulate a situation in which a participant's own arm was replaced by a robotic prosthetic arm, and... Read more
When AI-powered prosthetic arms that move autonomously become widespread, understanding how people feel about them and accept them will be crucial. In a study appearing in Scientific Reports, scientists used virtual reality to simulate a situation in which a participant's own arm was replaced by a robotic prosthetic arm, and... Read more -
Organic molecule stores solar energy for years, then releases it as heat on demand
 When the sun goes down, solar panels stop working. This is the fundamental hurdle of renewable energy: how to save the sun's power for a rainy day—or a cold night. Chemists at UC Santa Barbara have developed a solution that doesn't require bulky batteries or electrical grids. In a paper... Read more
When the sun goes down, solar panels stop working. This is the fundamental hurdle of renewable energy: how to save the sun's power for a rainy day—or a cold night. Chemists at UC Santa Barbara have developed a solution that doesn't require bulky batteries or electrical grids. In a paper... Read more -
New sound-based 3D-printing method enables finer, faster microdevices
 Concordia researchers have developed a new 3D-printing technique that uses sound waves to directly print tiny structures onto soft polymers like silicone with far greater precision than before. The approach, called proximal sound printing, opens new possibilities for manufacturing microscale devices used in health care, environmental monitoring and advanced sensors.... Read more
Concordia researchers have developed a new 3D-printing technique that uses sound waves to directly print tiny structures onto soft polymers like silicone with far greater precision than before. The approach, called proximal sound printing, opens new possibilities for manufacturing microscale devices used in health care, environmental monitoring and advanced sensors.... Read more -
Beyond the Fitbit: Why your next health tracker might be a button on your shirt
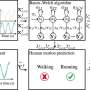 Measuring human movement with tracking devices on looser clothing is more accurate than on tight body suits or straps. This discovery by scientists at King's College London could mark a potential breakthrough for a range of technologies, including improving accuracy of personal health devices, such as Fitbits and smart watches,... Read more
Measuring human movement with tracking devices on looser clothing is more accurate than on tight body suits or straps. This discovery by scientists at King's College London could mark a potential breakthrough for a range of technologies, including improving accuracy of personal health devices, such as Fitbits and smart watches,... Read more -
Next-generation batteries could redefine the future of energy storage
 Drawing on an extensive survey of emerging battery chemistries and design innovations, researchers at the University of Sharjah are pointing to transformative technologies poised to meet the escalating energy demands of an increasingly electrified world.... Read more
Drawing on an extensive survey of emerging battery chemistries and design innovations, researchers at the University of Sharjah are pointing to transformative technologies poised to meet the escalating energy demands of an increasingly electrified world.... Read more -
Supercomputer provides high-fidelity insights into turbine aerothermal performance
 In a long-running collaboration with GE Aerospace, researchers at the University of Melbourne in Australia have been steadily working to improve the performance of high-pressure turbine (HPT) engines through computer simulations on leadership-class computing systems. These turbines are the heart of jet engines used in many commercial and military aircraft.... Read more
In a long-running collaboration with GE Aerospace, researchers at the University of Melbourne in Australia have been steadily working to improve the performance of high-pressure turbine (HPT) engines through computer simulations on leadership-class computing systems. These turbines are the heart of jet engines used in many commercial and military aircraft.... Read more -
AI and brain control: New system identifies animal behavior and silences responsible neurons in real time
 A male fruit fly in a laboratory chamber extends his wings and vibrates them to produce his species' version of a love song. A female fly stays nearby listening. Suddenly, a green light flashes across the chamber for a fraction of a second. The male's song cuts off mid-note and... Read more
A male fruit fly in a laboratory chamber extends his wings and vibrates them to produce his species' version of a love song. A female fly stays nearby listening. Suddenly, a green light flashes across the chamber for a fraction of a second. The male's song cuts off mid-note and... Read more -
Toward regenerative bioprinting: Magnetic mixer enables scalable manufacturing of 3D-printed tissues
 3D bioprinting, in which living tissues are printed with cells mixed into soft hydrogels, or "bio-inks," is widely used in the field of bioengineering for modeling or replacing the tissues in our bodies. The print quality and reproducibility of tissues, however, can face challenges. One of the most significant challenges... Read more
3D bioprinting, in which living tissues are printed with cells mixed into soft hydrogels, or "bio-inks," is widely used in the field of bioengineering for modeling or replacing the tissues in our bodies. The print quality and reproducibility of tissues, however, can face challenges. One of the most significant challenges... Read more -
New 3D-printing and manufacturing techniques grant more control over energetic material behavior
 Much like baking the perfect cake involves following a list of ingredients and instructions, manufacturing energetic materials—explosives, pyrotechnics and propellants—requires precise formulations, conditions and procedures to ensure they are safe and perform as intended.... Read more
Much like baking the perfect cake involves following a list of ingredients and instructions, manufacturing energetic materials—explosives, pyrotechnics and propellants—requires precise formulations, conditions and procedures to ensure they are safe and perform as intended.... Read more -
A forgotten battery design from Thomas Edison—how scientists helped reimagine it
 A little-known fact: In the year 1900, electric cars outnumbered gas-powered ones on the American road. The lead-acid auto battery of the time, courtesy of Thomas Edison, was expensive and had a range of only about 30 miles. Seeking to improve on this, Edison believed the nickel-iron battery was the... Read more
A little-known fact: In the year 1900, electric cars outnumbered gas-powered ones on the American road. The lead-acid auto battery of the time, courtesy of Thomas Edison, was expensive and had a range of only about 30 miles. Seeking to improve on this, Edison believed the nickel-iron battery was the... Read more -
Harnessing degradation: Researchers pave way for more precise, responsive shape morphing implants
 An international research team has demonstrated a new approach to 4D-printed shape-morphing implants that opens the door to increasingly personalized health care. The findings, outlined in the journal Additive Manufacturing, highlight how material degradation can be used to trigger controlled shape change of implanted material.... Read more
An international research team has demonstrated a new approach to 4D-printed shape-morphing implants that opens the door to increasingly personalized health care. The findings, outlined in the journal Additive Manufacturing, highlight how material degradation can be used to trigger controlled shape change of implanted material.... Read more -
Scientists camouflage heart rate from invasive radar-based surveillance
 It's a typical workday and you sign onto your computer. Unbeknownst to you, a high-frequency sensing system embedded in your work device is now tracking your heart rate, allowing your employer to monitor your breaks, engagement, and stress levels and infer alertness. It sounds like a dystopian scenario, but some... Read more
It's a typical workday and you sign onto your computer. Unbeknownst to you, a high-frequency sensing system embedded in your work device is now tracking your heart rate, allowing your employer to monitor your breaks, engagement, and stress levels and infer alertness. It sounds like a dystopian scenario, but some... Read more -
Rotating nozzle 3D printing creates air-powered soft robots with preset bends
 Soft robots made out of flexible, biocompatible materials are in high demand in industries from health care to manufacturing, but precisely designing and controlling such robots for specific purposes is a perennial challenge. What if you could 3D print a soft robot with predictable shape-morphing capabilities already built in? Harvard... Read more
Soft robots made out of flexible, biocompatible materials are in high demand in industries from health care to manufacturing, but precisely designing and controlling such robots for specific purposes is a perennial challenge. What if you could 3D print a soft robot with predictable shape-morphing capabilities already built in? Harvard... Read more -
Power at the micrometer scale: A battery built for the smallest machines
 Sensors small enough to disappear into the body, microrobots that move without wires, and smart systems hidden inside everyday materials—all require a battery to function. As electronics shrink towards the micrometer scale, conventional batteries become bulky, impractical, or impossible to integrate into these tiny devices.... Read more
Sensors small enough to disappear into the body, microrobots that move without wires, and smart systems hidden inside everyday materials—all require a battery to function. As electronics shrink towards the micrometer scale, conventional batteries become bulky, impractical, or impossible to integrate into these tiny devices.... Read more -
Low-temperature, sinterless silica glass developed using 3D printing techniques
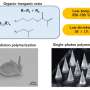 A research team has used advanced 3D printing techniques to develop low-temperature, "sinterless" silica glass. They converted 3D-printed objects into silica glass structures at significantly lower temperatures than traditional sintering, offering a promising route for efficient and precise glass manufacturing. Their research is published in the journal Polymers.... Read more
A research team has used advanced 3D printing techniques to develop low-temperature, "sinterless" silica glass. They converted 3D-printed objects into silica glass structures at significantly lower temperatures than traditional sintering, offering a promising route for efficient and precise glass manufacturing. Their research is published in the journal Polymers.... Read more -
Hair-thin silica fiber microphone detects ultrasound from 40 kHz to 1.6 MHz
 Researchers have fabricated a hair-thin microphone made entirely of silica fiber that can detect a large range of ultrasound frequencies beyond the reach of the human ear. Able to withstand temperatures up to 1,000°C, the device could eventually be used inside high-voltage transformers to detect early signs of failure before... Read more
Researchers have fabricated a hair-thin microphone made entirely of silica fiber that can detect a large range of ultrasound frequencies beyond the reach of the human ear. Able to withstand temperatures up to 1,000°C, the device could eventually be used inside high-voltage transformers to detect early signs of failure before... Read more -
Dynamic digital product passports for short-shelf-life food and drink could cut waste and improve safety
 Dynamic digital product passports—real-time, intelligent digital records that capture the true condition of perishable goods such as food and drink throughout their life cycle—could dramatically cut waste and improve safety, thanks to a new framework jointly developed by researchers at the University of Surrey and King's College London.... Read more
Dynamic digital product passports—real-time, intelligent digital records that capture the true condition of perishable goods such as food and drink throughout their life cycle—could dramatically cut waste and improve safety, thanks to a new framework jointly developed by researchers at the University of Surrey and King's College London.... Read more -
New AI system pushes the time limits of generative video
 A team of EPFL researchers has taken a major step towards resolving the problem of drift in generative video, which is what causes sequences to become incoherent after a handful of seconds. Their breakthrough paves the way to AI videos with no time constraints.... Read more
A team of EPFL researchers has taken a major step towards resolving the problem of drift in generative video, which is what causes sequences to become incoherent after a handful of seconds. Their breakthrough paves the way to AI videos with no time constraints.... Read more -
Researchers successfully 3D print one of industry's hardest engineering materials
 Tungsten carbide–cobalt (WC–Co) is prized for its hardness, but that same property makes it unusually difficult to shape. The current process is wasteful and expensive for the yield produced, and an economically sensible method for creating these materials is long overdue.... Read more
Tungsten carbide–cobalt (WC–Co) is prized for its hardness, but that same property makes it unusually difficult to shape. The current process is wasteful and expensive for the yield produced, and an economically sensible method for creating these materials is long overdue.... Read more -
AI agents debate more effectively when given personalities and the ability to interrupt
 In a typical online meeting, humans don't always wait politely for their turn to speak. They interrupt to express strong agreement, stay silent when they are unsure, and let their personalities shape the flow of the discussion. Yet, when artificial intelligence (AI) agents are programmed to debate or collaborate, they... Read more
In a typical online meeting, humans don't always wait politely for their turn to speak. They interrupt to express strong agreement, stay silent when they are unsure, and let their personalities shape the flow of the discussion. Yet, when artificial intelligence (AI) agents are programmed to debate or collaborate, they... Read more -
Virtual reality demonstrates the 'honey-pot effect' in pedestrian attention to public displays
 Researchers at University of Tsukuba have used virtual reality (VR) to demonstrate that pedestrians' behaviors, such as stopping or turning their heads, can induce gaze following (the "honey-pot effect") among individuals walking behind them, thereby substantially increasing awareness of nearby public displays. However, these socially driven, momentary glances rarely result... Read more
Researchers at University of Tsukuba have used virtual reality (VR) to demonstrate that pedestrians' behaviors, such as stopping or turning their heads, can induce gaze following (the "honey-pot effect") among individuals walking behind them, thereby substantially increasing awareness of nearby public displays. However, these socially driven, momentary glances rarely result... Read more
© 2024 CanadianReporter.ca | The Latest From Canada - The Great White North.
