-
A rewritable DNA hard drive may help solve the growing data storage crisis
 Around the world, scientists are exploring an unexpected solution to the growing data crisis: storing digital information in synthetic DNA. The idea is simple but powerful—DNA is one of the most compact, durable information systems on Earth. But one issue has held the field back. Once data is written into... Read more
Around the world, scientists are exploring an unexpected solution to the growing data crisis: storing digital information in synthetic DNA. The idea is simple but powerful—DNA is one of the most compact, durable information systems on Earth. But one issue has held the field back. Once data is written into... Read more -
Researchers pioneer next-generation AI semiconductors with 'thermal constraining' technique
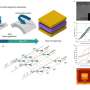 A research team led by Professor Taesung Kim from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University has developed a technology that precisely controls the internal structure of semiconductors using heat, much like stamping out "bungeoppang" (fish-shaped pastry) in a mold. The team report that this approach improves the performance... Read more
A research team led by Professor Taesung Kim from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Sungkyunkwan University has developed a technology that precisely controls the internal structure of semiconductors using heat, much like stamping out "bungeoppang" (fish-shaped pastry) in a mold. The team report that this approach improves the performance... Read more -
Miniaturized radar chip developed for next-generation wireless networks
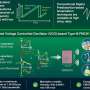 A miniaturized radar chip, developed by researchers at Science Tokyo, advances Integrated Sensing and Communication for Beyond 5G and 6G systems. Measuring just 0.24 mm2 and consuming only 9.8 mW, the compact, low-power device generates high-speed, highly linear chirps by embedding linearization directly into the hardware, overcoming traditional speed-versus-accuracy limits... Read more
A miniaturized radar chip, developed by researchers at Science Tokyo, advances Integrated Sensing and Communication for Beyond 5G and 6G systems. Measuring just 0.24 mm2 and consuming only 9.8 mW, the compact, low-power device generates high-speed, highly linear chirps by embedding linearization directly into the hardware, overcoming traditional speed-versus-accuracy limits... Read more -
Atom-thin ferroelectric transistor can store 3,024 polarization states
 Over the past few decades, electronics engineers have been trying to develop new neuromorphic hardware, systems that mirror the organization of neurons in the human brain. These systems could run artificial intelligence (AI) models, particularly artificial neural networks (ANNs) more reliably and efficiently than existing devices.... Read more
Over the past few decades, electronics engineers have been trying to develop new neuromorphic hardware, systems that mirror the organization of neurons in the human brain. These systems could run artificial intelligence (AI) models, particularly artificial neural networks (ANNs) more reliably and efficiently than existing devices.... Read more -
Bio-inspired chip helps robots and self-driving cars react faster to movement
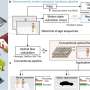 Robots and self-driving cars could soon benefit from a new kind of brain-inspired hardware that can allegedly detect movement and react faster than a human. A new study published in the journal Nature Communications details how an international team built their neuromorphic temporal-attention hardware system to speed up automated driving... Read more
Robots and self-driving cars could soon benefit from a new kind of brain-inspired hardware that can allegedly detect movement and react faster than a human. A new study published in the journal Nature Communications details how an international team built their neuromorphic temporal-attention hardware system to speed up automated driving... Read more -
Ultrafast nanolasers mimic how the brain imagines unseen parts of the world
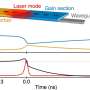 A new study has demonstrated how networks of spiking nanolasers could emulate a key principle of brain function: to imagine things that we cannot directly perceive by sampling from internal models of the world. The study, led by scientists from the University of Bern in collaboration with Thales Research &... Read more
A new study has demonstrated how networks of spiking nanolasers could emulate a key principle of brain function: to imagine things that we cannot directly perceive by sampling from internal models of the world. The study, led by scientists from the University of Bern in collaboration with Thales Research &... Read more -
How bee brains are shaping next-generation computer chips
 Bees navigate their surroundings with astonishing precision. Their brains are now inspiring the design of tiny, low-power chips that could one day guide miniature robots and sensors.... Read more
Bees navigate their surroundings with astonishing precision. Their brains are now inspiring the design of tiny, low-power chips that could one day guide miniature robots and sensors.... Read more -
Brain-inspired hardware uses single-spike coding to run AI more efficiently
 The use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, such as the models underpinning the functioning of ChatGPT and various other online platforms, has grown exponentially over the past few years. Current hardware and electronic devices, however, might not be best suited for running these systems, which are computationally intensive and can... Read more
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) systems, such as the models underpinning the functioning of ChatGPT and various other online platforms, has grown exponentially over the past few years. Current hardware and electronic devices, however, might not be best suited for running these systems, which are computationally intensive and can... Read more -
Analog hardware may solve Internet of Things' speed bumps and bottlenecks
 The ubiquity of smart devices—not just phones and watches, but lights, refrigerators, doorbells and more, all constantly recording and transmitting data—is creating massive volumes of digital information that drain energy and slow data transmission speeds. With the rising use of artificial intelligence in industries ranging from health care and finance... Read more
The ubiquity of smart devices—not just phones and watches, but lights, refrigerators, doorbells and more, all constantly recording and transmitting data—is creating massive volumes of digital information that drain energy and slow data transmission speeds. With the rising use of artificial intelligence in industries ranging from health care and finance... Read more -
New smart chip reduces consumption and computing time, advancing high-performance computing
 A new chip aims to dramatically reduce energy consumption while accelerating the processing of large amounts of data.... Read more
A new chip aims to dramatically reduce energy consumption while accelerating the processing of large amounts of data.... Read more -
New memristor training method slashes AI energy use by six orders of magnitude
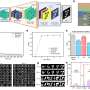 In a Nature Communications study, researchers from China have developed an error-aware probabilistic update (EaPU) method that aligns memristor hardware's noisy updates with neural network training, slashing energy use by nearly six orders of magnitude versus GPUs while boosting accuracy on vision tasks. The study validates EaPU on 180 nm... Read more
In a Nature Communications study, researchers from China have developed an error-aware probabilistic update (EaPU) method that aligns memristor hardware's noisy updates with neural network training, slashing energy use by nearly six orders of magnitude versus GPUs while boosting accuracy on vision tasks. The study validates EaPU on 180 nm... Read more -
Reinforcement learning accelerates model-free training of optical AI systems
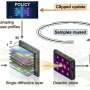 Optical computing has emerged as a powerful approach for high-speed and energy-efficient information processing. Diffractive optical networks, in particular, enable large-scale parallel computation through the use of passive structured phase masks and the propagation of light. However, one major challenge remains: systems trained in model-based simulations often fail to perform... Read more
Optical computing has emerged as a powerful approach for high-speed and energy-efficient information processing. Diffractive optical networks, in particular, enable large-scale parallel computation through the use of passive structured phase masks and the propagation of light. However, one major challenge remains: systems trained in model-based simulations often fail to perform... Read more -
Turning PCs and mobile devices into AI infrastructure can slash operational costs
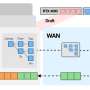 Until now, AI services based on large language models (LLMs) have mostly relied on expensive data center GPUs. This has resulted in high operational costs and created a significant barrier to entry for utilizing AI technology. A research team at KAIST has developed a technology that reduces reliance on expensive... Read more
Until now, AI services based on large language models (LLMs) have mostly relied on expensive data center GPUs. This has resulted in high operational costs and created a significant barrier to entry for utilizing AI technology. A research team at KAIST has developed a technology that reduces reliance on expensive... Read more -
New ultrathin ferroelectric capacitors show promise for compact memory devices
 An ultrathin ferroelectric capacitor, designed by researchers from Japan, demonstrates strong electric polarization despite being just 30 nm thick including top and bottom electrodes—making it suitable for high-density electronics. Using a scandium-doped aluminum nitride film as the ferroelectric layer, the team achieved high remanent polarization even at reduced thicknesses. This... Read more
An ultrathin ferroelectric capacitor, designed by researchers from Japan, demonstrates strong electric polarization despite being just 30 nm thick including top and bottom electrodes—making it suitable for high-density electronics. Using a scandium-doped aluminum nitride film as the ferroelectric layer, the team achieved high remanent polarization even at reduced thicknesses. This... Read more -
All-optical chip achieves 100-fold speed boost over top-tier NVIDIA chips
 Scientists in China have unveiled a new AI chip called LightGen that is 100 times faster and 100 times more energy efficient than NVIDIA chips, the leading supplier of AI chips worldwide. Instead of using electricity to move information, this new optical chip relies on light to perform complex generative... Read more
Scientists in China have unveiled a new AI chip called LightGen that is 100 times faster and 100 times more energy efficient than NVIDIA chips, the leading supplier of AI chips worldwide. Instead of using electricity to move information, this new optical chip relies on light to perform complex generative... Read more -
New memristor-based converter boosts energy efficiency in AI hardware
 A cross-institutional team led by researchers from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EEE), under the Faculty of Engineering at The University of Hong Kong (HKU), have achieved a major breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware by developing a new type of analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that... Read more
A cross-institutional team led by researchers from the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EEE), under the Faculty of Engineering at The University of Hong Kong (HKU), have achieved a major breakthrough in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) hardware by developing a new type of analog-to-digital converter (ADC) that... Read more -
First monolithic 3D chip built in U.S. foundry delivers major AI speed gains
 A collaborative team has achieved the first monolithic 3D chip built in a U.S. foundry, delivering the densest 3D chip wiring and order-of-magnitude speed gains.... Read more
A collaborative team has achieved the first monolithic 3D chip built in a U.S. foundry, delivering the densest 3D chip wiring and order-of-magnitude speed gains.... Read more -
New materials could boost the energy efficiency of microelectronics
 MIT researchers have developed a new fabrication method that could enable the production of more energy efficient electronics by stacking multiple functional components on top of one existing circuit.... Read more
MIT researchers have developed a new fabrication method that could enable the production of more energy efficient electronics by stacking multiple functional components on top of one existing circuit.... Read more -
Fully digital design paves the way for scalable probabilistic computing
 Artificial intelligence and machine learning could become dramatically more efficient, thanks to a new type of computer component developed by researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara and Tohoku University, in collaboration with the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC).... Read more
Artificial intelligence and machine learning could become dramatically more efficient, thanks to a new type of computer component developed by researchers at the University of California, Santa Barbara and Tohoku University, in collaboration with the Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC).... Read more -
AI headphones automatically learn who you're talking to—and let you hear them better
 Holding a conversation in a crowded room often leads to the frustrating "cocktail party problem," or the challenge of separating the voices of conversation partners from a hubbub. It's a mentally taxing situation that can be exacerbated by hearing impairment.... Read more
Holding a conversation in a crowded room often leads to the frustrating "cocktail party problem," or the challenge of separating the voices of conversation partners from a hubbub. It's a mentally taxing situation that can be exacerbated by hearing impairment.... Read more -
Data centers: a view from the inside
 The expansion of data centers to power the AI boom has more people wondering: what exactly is in a data center?... Read more
The expansion of data centers to power the AI boom has more people wondering: what exactly is in a data center?... Read more -
Team develops chips that act like brains and makes them scalable
 Developing chips that simulate how the brain works has great promise for AI, robotics, and other fields. But making them so that they're scalable while providing repeatable results has proven tricky. Now, a Yale-led team of researchers has put forth a solution. The results are published in Nature Communications.... Read more
Developing chips that simulate how the brain works has great promise for AI, robotics, and other fields. But making them so that they're scalable while providing repeatable results has proven tricky. Now, a Yale-led team of researchers has put forth a solution. The results are published in Nature Communications.... Read more -
Engineers develop thin film to make AI chips faster and more energy efficient
 Addressing the staggering power and energy demands of artificial intelligence, engineers at the University of Houston have developed a revolutionary new thin-film material that promises to make AI devices significantly faster while dramatically cutting energy consumption.... Read more
Addressing the staggering power and energy demands of artificial intelligence, engineers at the University of Houston have developed a revolutionary new thin-film material that promises to make AI devices significantly faster while dramatically cutting energy consumption.... Read more -
Amazon unveils new AI chip in battle against Nvidia
 Amazon Web Services launched its in-house-built Trainium3 AI chip on Tuesday, marking a significant push to compete with Nvidia in the lucrative market for artificial intelligence computing power.... Read more
Amazon Web Services launched its in-house-built Trainium3 AI chip on Tuesday, marking a significant push to compete with Nvidia in the lucrative market for artificial intelligence computing power.... Read more -
Mexico unveils plan to build Latin America's biggest supercomputer
 The Mexican government will build a supercomputer with a processing capacity seven times greater than the current most powerful computer in Latin America, officials responsible for the project said Wednesday.... Read more
The Mexican government will build a supercomputer with a processing capacity seven times greater than the current most powerful computer in Latin America, officials responsible for the project said Wednesday.... Read more -
ULTRARAM beyond the lab: The gap between elegant physics and commercial viability
 Recent research from a University of Adelaide academic has outlined the gap between scientific reality and whether a promising technology reaches commercial production. Adjunct Lecturer Dr. Dominic Lane, School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, has been exploring the world of ULTRARAM, a widely promoted III–V semiconductor memory concept claimed to... Read more
Recent research from a University of Adelaide academic has outlined the gap between scientific reality and whether a promising technology reaches commercial production. Adjunct Lecturer Dr. Dominic Lane, School of Electrical and Mechanical Engineering, has been exploring the world of ULTRARAM, a widely promoted III–V semiconductor memory concept claimed to... Read more -
Integrated photonic millimeter-wave radar chip developed for next-generation radar 6G networks
 In a breakthrough in radar technology, researchers from the City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) have developed the world's first integrated photonic millimeter-wave radar chip, achieving unprecedented precision in a remarkably compact device. This breakthrough represents a significant step forward in the development of Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) networks,... Read more
In a breakthrough in radar technology, researchers from the City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) have developed the world's first integrated photonic millimeter-wave radar chip, achieving unprecedented precision in a remarkably compact device. This breakthrough represents a significant step forward in the development of Integrated Sensing and Communication (ISAC) networks,... Read more -
A new route to optimize AI hardware: Homodyne gradient extraction
 A team led by the BRAINS Center for Brain-Inspired Computing at the University of Twente has demonstrated a new way to make electronic materials adapt in a manner comparable to machine learning. Their study, published in Nature Communications, introduces a method for physical learning that does not require software algorithms... Read more
A team led by the BRAINS Center for Brain-Inspired Computing at the University of Twente has demonstrated a new way to make electronic materials adapt in a manner comparable to machine learning. Their study, published in Nature Communications, introduces a method for physical learning that does not require software algorithms... Read more -
Smarter AI processing for cleaner air: A blueprint to cut pollution and prolong server life
 As artificial intelligence becomes more powerful and widespread, so does the environmental cost of running it. Behind every chatbot, image generator, and television streaming recommendation are massive banks of millions of computers housed in an increasing number of data centers that consume staggering amounts of electricity and water to keep... Read more
As artificial intelligence becomes more powerful and widespread, so does the environmental cost of running it. Behind every chatbot, image generator, and television streaming recommendation are massive banks of millions of computers housed in an increasing number of data centers that consume staggering amounts of electricity and water to keep... Read more -
A brain-like chip interprets neural network connectivity in real time
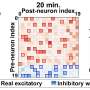 The ability to analyze the brain's neural connectivity is emerging as a key foundation for brain-computer interface (BCI) technologies, such as controlling artificial limbs and enhancing human intelligence. To make these analyses more precise, it is critical to quickly and accurately interpret the complex signals from many neurons in the... Read more
The ability to analyze the brain's neural connectivity is emerging as a key foundation for brain-computer interface (BCI) technologies, such as controlling artificial limbs and enhancing human intelligence. To make these analyses more precise, it is critical to quickly and accurately interpret the complex signals from many neurons in the... Read more -
Germany hopes new data center can help bring 'digital sovereignty'
 A new mega data center is slated to rise in a rural stretch of eastern Germany in what backers hope is a starting point for a European AI sector that can compete with the United States and China.... Read more
A new mega data center is slated to rise in a rural stretch of eastern Germany in what backers hope is a starting point for a European AI sector that can compete with the United States and China.... Read more -
Artificial neuron can mimic different parts of the brain—a major step toward human-like robotics
 Robots that can sense and respond to the world like humans may soon be a reality as scientists have created an artificial neuron capable of mimicking different parts of the brain.... Read more
Robots that can sense and respond to the world like humans may soon be a reality as scientists have created an artificial neuron capable of mimicking different parts of the brain.... Read more -
Novel memristor wafer integration technology paves the way for brain-like AI chips
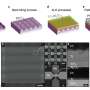 A research team led by Professor Sanghyeon Choi from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at DGIST has successfully developed a memristor, which is gaining recognition as a next-generation semiconductor device, through mass-integration at the wafer scale.... Read more
A research team led by Professor Sanghyeon Choi from the Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science at DGIST has successfully developed a memristor, which is gaining recognition as a next-generation semiconductor device, through mass-integration at the wafer scale.... Read more -
Scalable memtransistor arrays show potential for energy-efficient artificial neural networks
 Researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have fabricated ultra-thin memtransistor arrays from two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDC) with controllable Schottky barriers. These arrays are highly uniform, demonstrating low device-to-device variation and provide high performance for image recognition tasks.... Read more
Researchers at the National University of Singapore (NUS) have fabricated ultra-thin memtransistor arrays from two-dimensional (2D) transition metal dichalcogenide (TMDC) with controllable Schottky barriers. These arrays are highly uniform, demonstrating low device-to-device variation and provide high performance for image recognition tasks.... Read more -
RRAM-based analog computing system rapidly solves matrix equations with high precision
 Analog computers are systems that perform computations by manipulating physical quantities such as electrical current, that map math variables, instead of representing information using abstraction with discrete binary values (i.e., 0 or 1), like digital computers.... Read more
Analog computers are systems that perform computations by manipulating physical quantities such as electrical current, that map math variables, instead of representing information using abstraction with discrete binary values (i.e., 0 or 1), like digital computers.... Read more -
Neuromorphic computer prototype learns patterns with fewer computations than traditional AI
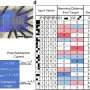 Could computers ever learn more like humans do, without relying on artificial intelligence (AI) systems that must undergo extremely expensive training?... Read more
Could computers ever learn more like humans do, without relying on artificial intelligence (AI) systems that must undergo extremely expensive training?... Read more -
AI efficiency advances with spintronic memory chip that combines storage and processing
 To make accurate predictions and reliably complete desired tasks, most artificial intelligence (AI) systems need to rapidly analyze large amounts of data. This currently entails the transfer of data between processing and memory units, which are separate in existing electronic devices.... Read more
To make accurate predictions and reliably complete desired tasks, most artificial intelligence (AI) systems need to rapidly analyze large amounts of data. This currently entails the transfer of data between processing and memory units, which are separate in existing electronic devices.... Read more -
Beyond electronics: Optical system performs feature extraction with unprecedented low latency
 Many modern artificial intelligence (AI) applications, such as surgical robotics and real-time financial trading, depend on the ability to quickly extract key features from streams of raw data. This process is currently bottlenecked by traditional digital processors. The physical limits of conventional electronics prevent the reduction in latency and the... Read more
Many modern artificial intelligence (AI) applications, such as surgical robotics and real-time financial trading, depend on the ability to quickly extract key features from streams of raw data. This process is currently bottlenecked by traditional digital processors. The physical limits of conventional electronics prevent the reduction in latency and the... Read more -
Unified memristor-ferroelectric memory developed for energy-efficient training of AI systems
 Over the past decades, electronics engineers have developed a wide range of memory devices that can safely and efficiently store increasing amounts of data. However, the different types of devices developed to date come with their own trade-offs, which pose limits on their overall performance and restrict their possible applications.... Read more
Over the past decades, electronics engineers have developed a wide range of memory devices that can safely and efficiently store increasing amounts of data. However, the different types of devices developed to date come with their own trade-offs, which pose limits on their overall performance and restrict their possible applications.... Read more -
Reinventing computer technology for the benefit of data centers
 In the largest computer systems project ever undertaken at EPFL, an international team of researchers has come up with a new way of building computers to help tackle the increasing challenges faced by data centers.... Read more
In the largest computer systems project ever undertaken at EPFL, an international team of researchers has come up with a new way of building computers to help tackle the increasing challenges faced by data centers.... Read more -
Team develops high-speed, ultra-low-power superconductive neuron device
 A research team has developed a neuron device that holds potential for application in large-scale, high-speed superconductive neural network circuits. The device operates at high speeds with ultra-low-power consumption and is tolerant to parameter fluctuations during circuit fabrication.... Read more
A research team has developed a neuron device that holds potential for application in large-scale, high-speed superconductive neural network circuits. The device operates at high speeds with ultra-low-power consumption and is tolerant to parameter fluctuations during circuit fabrication.... Read more -
Group including Nvidia, BlackRock buying Aligned Data Centers in deal worth about $40 billion
 A group including BlackRock, Nvidia and Microsoft is buying Aligned Data Centers in an approximately $40 billion deal in an effort to expand next-generation cloud and artificial intelligence infrastructure.... Read more
A group including BlackRock, Nvidia and Microsoft is buying Aligned Data Centers in an approximately $40 billion deal in an effort to expand next-generation cloud and artificial intelligence infrastructure.... Read more -
AI-powered method helps protect global chip supply chains from cyber threats
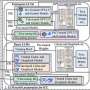 University of Missouri researchers have used artificial intelligence to detect hidden hardware trojans through a method that's 97% accurate.... Read more
University of Missouri researchers have used artificial intelligence to detect hidden hardware trojans through a method that's 97% accurate.... Read more -
Vulnerability in confidential cloud environments uncovered
 Some data is so sensitive that it is processed only in specially protected cloud areas. These are designed to ensure that not even a cloud provider can access the data. ETH Zurich researchers have now found a vulnerability that could allow hackers to breach these confidential environments.... Read more
Some data is so sensitive that it is processed only in specially protected cloud areas. These are designed to ensure that not even a cloud provider can access the data. ETH Zurich researchers have now found a vulnerability that could allow hackers to breach these confidential environments.... Read more -
Next-generation memory: Tungsten-based SOT-MRAM achieves nanosecond switching and low-power data storage
 The ability to reliably switch the direction of magnetic alignment in materials, a process known as magnetization switching, is known to be central to the functioning of most memory devices. One known strategy to achieve entails the creation of a rotational force (i.e., torque) on electron spins via an electric... Read more
The ability to reliably switch the direction of magnetic alignment in materials, a process known as magnetization switching, is known to be central to the functioning of most memory devices. One known strategy to achieve entails the creation of a rotational force (i.e., torque) on electron spins via an electric... Read more -
AI tools can help hackers plant hidden flaws in computer chips, study finds
 Widely available artificial intelligence systems can be used to deliberately insert hard-to-detect security vulnerabilities into the code that defines computer chips, according to new research from the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, a warning about the potential weaponization of AI in hardware design.... Read more
Widely available artificial intelligence systems can be used to deliberately insert hard-to-detect security vulnerabilities into the code that defines computer chips, according to new research from the NYU Tandon School of Engineering, a warning about the potential weaponization of AI in hardware design.... Read more -
New haptic system lets soft objects respond to taps, squeezes and twists
 New technology that invites expressive, two-way communication between a person and the soft, flexible object they are holding or wearing has been developed at the University of Bath.... Read more
New technology that invites expressive, two-way communication between a person and the soft, flexible object they are holding or wearing has been developed at the University of Bath.... Read more -
Hardware vulnerability allows attackers to hack AI training data
 Researchers from NC State University have identified the first hardware vulnerability that allows attackers to compromise the data privacy of artificial intelligence (AI) users by exploiting the physical hardware on which AI is run.... Read more
Researchers from NC State University have identified the first hardware vulnerability that allows attackers to compromise the data privacy of artificial intelligence (AI) users by exploiting the physical hardware on which AI is run.... Read more -
Back to the future: Is light-speed analog computing on the horizon?
 Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in analog computing, developing a programmable electronic circuit that harnesses the properties of high-frequency electromagnetic waves to perform complex parallel processing at light-speed.... Read more
Scientists have achieved a breakthrough in analog computing, developing a programmable electronic circuit that harnesses the properties of high-frequency electromagnetic waves to perform complex parallel processing at light-speed.... Read more -
The lord of the ring mouse—a lightweight, ring-based computer mouse lasts over a month on a single charge
 As the use of wearable devices such as augmented reality (AR) glasses has slowly but steadily increased, so too has the desire to control these devices in an easy and convenient way. Ring controllers worn on the finger already exist, but usually have some drawbacks in their size, weight or... Read more
As the use of wearable devices such as augmented reality (AR) glasses has slowly but steadily increased, so too has the desire to control these devices in an easy and convenient way. Ring controllers worn on the finger already exist, but usually have some drawbacks in their size, weight or... Read more
© 2024 CanadianReporter.ca | The Latest From Canada - The Great White North.
